
The first column of a z table contains the z score up to the first decimal place. This table tells you the total area under the curve up to a given z score-this area is equal to the probability of values below that z score occurring. Here, we use a portion of the cumulative table. There are a few different formats for the z table.

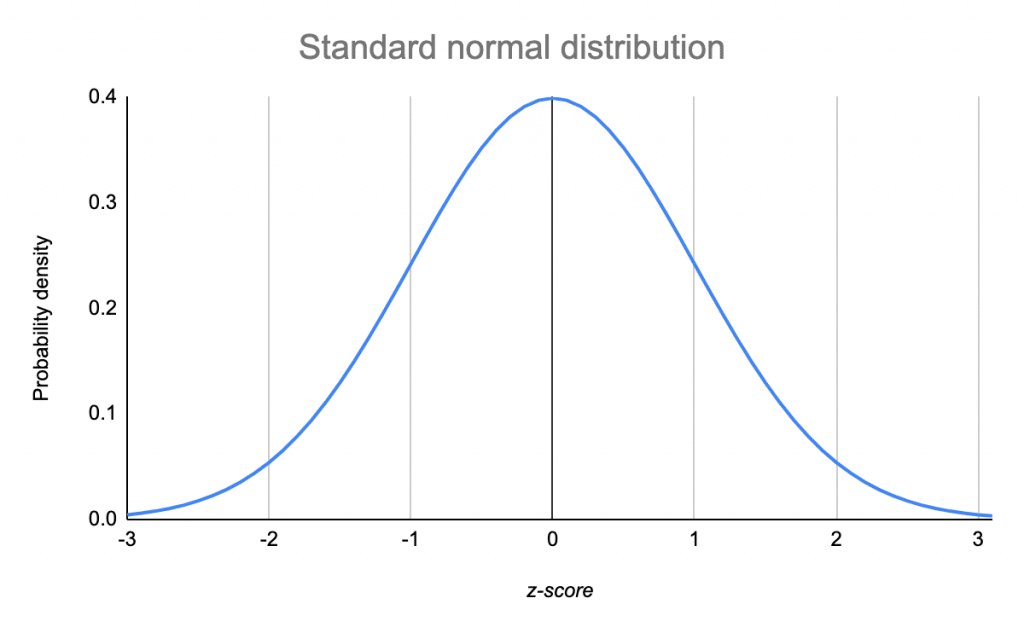
In a z table, the area under the curve is reported for every z value between -4 and 4 at intervals of 0.01. Once you have a z score, you can look up the corresponding probability in a z table. Usually, a p value of 0.05 or less means that your results are unlikely to have arisen by chance it indicates a statistically significant effect.īy converting a value in a normal distribution into a z score, you can easily find the p value for a z test. The area under the curve to the right of a z score is the p value, and it’s the likelihood of your observation occurring if the null hypothesis is true. Its null hypothesis typically assumes no difference between groups. The z test is used to compare the means of two groups, or to compare the mean of a group to a set value. The z score is the test statistic used in a z test. This is the area under the curve left or right of that z score. The total area under the curve is 1 or 100%.Įvery z score has an associated p value that tells you the probability of all values below or above that z score occuring. The standard normal distribution is a probability distribution, so the area under the curve between two points tells you the probability of variables taking on a range of values. Use the standard normal distribution to find probability Next, we can find the probability of this score using a z table. That means 1380 is 1.53 standard deviations from the mean of your distribution. Step 2: Divide the difference by the standard deviation. Step 1: Subtract the mean from the x value. The z score tells you how many standard deviations away 1380 is from the mean. To standardize your data, you first find the z score for 1380. You want to find the probability that SAT scores in your sample exceed 1380. The data follows a normal distribution with a mean score ( M) of 1150 and a standard deviation ( SD) of 150. Divide the difference by the standard deviation.Įxample: Finding a z scoreYou collect SAT scores from students in a new test preparation course.Subtract the mean from your individual value.To standardize a value from a normal distribution, convert the individual value into a z-score: Find the probability that a sample mean significantly differs from a known population mean.Find the probability of observations in a distribution falling above or below a given value.Normalize scores for statistical decision-making (e.g., grading on a curve).Compare scores on different distributions with different means and standard deviations.A z score of zero means that your x value is equal to the mean.Ĭonverting a normal distribution into the standard normal distribution allows you to:.A negative z score means that your x value is less than the mean.A positive z score means that your x value is greater than the mean.A z score is a standard score that tells you how many standard deviations away from the mean an individual value ( x) lies: While data points are referred to as x in a normal distribution, they are called z or z scores in the z distribution. This allows you to easily calculate the probability of certain values occurring in your distribution, or to compare data sets with different means and standard deviations. When you standardize a normal distribution, the mean becomes 0 and the standard deviation becomes 1. See editing example Standardizing a normal distribution Position or shape (relative to standard normal distribution) A small standard deviation results in a narrow curve, while a large standard deviation leads to a wide curve. The standard deviation stretches or squeezes the curve. Increasing the mean moves the curve right, while decreasing it moves the curve left. The mean determines where the curve is centered. In the standard normal distribution, the mean and standard deviation are always fixed.Įvery normal distribution is a version of the standard normal distribution that’s been stretched or squeezed and moved horizontally right or left. However, a normal distribution can take on any value as its mean and standard deviation. Normal distribution vs the standard normal distributionĪll normal distributions, like the standard normal distribution, are unimodal and symmetrically distributed with a bell-shaped curve. You can calculate the standard normal distribution with our calculator below. Frequently asked questions about the standard normal distribution.Step-by-step example of using the z distribution.Use the standard normal distribution to find probability.Normal distribution vs the standard normal distribution.Standard normal distribution calculator.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
